Red-throated Lorikeet Vini amabilis Scientific name definitions
- CR Critically Endangered
- Names (18)
- Monotypic
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Catalan | lori gorja-roig |
| Czech | charmozin rudokrký |
| Dutch | Roodkeellori |
| English | Red-throated Lorikeet |
| English (United States) | Red-throated Lorikeet |
| French | Lori à gorge rouge |
| French (France) | Lori à gorge rouge |
| German | Rotschenkellori |
| Japanese | アカズボンインコ |
| Norwegian | rødstrupelori |
| Polish | lorika czerwonogardła |
| Serbian | Crvenobradi lori |
| Slovak | lori nektárový |
| Spanish | Lori Gorjirrojo |
| Spanish (Spain) | Lori gorjirrojo |
| Swedish | rödstrupig lorikit |
| Turkish | Kırmızı Gerdanlı Loriket |
| Ukrainian | Лорікет червоногорлий |
Vini amabilis Ramsay, 1875
Definitions
- VINI
- vini
- amabile / amabilis
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Field Identification
Systematics History
Subspecies
Distribution
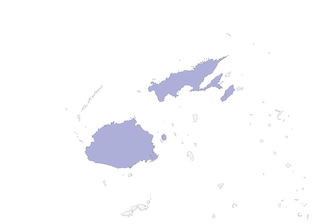
Fiji: on Vanua Levu, Taveuni, Viti Levu and Ovalau. None of these islands known, with certainty, to possess extant populations.
Habitat
Movement
Diet and Foraging
Sounds and Vocal Behavior
Vocalizations similar to those of other members of the genus, i.e. short, high-pitched shrill notes uttered while feeding or in flight.
Breeding
Conservation Status
CRITICALLY ENDANGERED. CITES II. Restricted-range species: present in Fiji EBA. Considered common when first collected on Ovalau in 1875 (2), but otherwise appears to have always been rare. The only confirmed records since 19th century have been from Viti Levu, where only small flocks of up to six birds have been seen. Last recorded by observers familiar with the species in 1993, although there are further well-documented sightings as recently as 2002. However, a 49-day survey on Viti Levu in 2001–2002 failed to locate birds, nor was it found during more recent surveys BirdLife International (2015) Species factsheet: Charmosyna amabilis. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 16/04/2015. . Outside Viti Levu, there are unconfirmed records from the 1980s and 1990s from Ovalau, Taveuni and Vanua Levu, but surveys in 2003 likewise failed to find any birds. On the basis of these searches it is estimated that its total population may number fewer than 50 birds BirdLife International (2015) Species factsheet: Charmosyna amabilis. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 16/04/2015. . The cause of the decline on or loss from other islands is not known but may be predation by black rats (Rattus rattus), exacerbated by widespread deforestation. Not considered of conservation concern until 1994, since when its threat category has been progressively elevated.
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding




























